- M Lab. TOP
- New Technology Projects
- Phosphors
Phosphors
Our phosphors are functional materials
that convert blue LED light into green and red.
Product Information
Overview
Our phosphors are functional materials that convert blue LED light
into green and red.
They were developed for micro- and mini-LED displays.

Characteristics
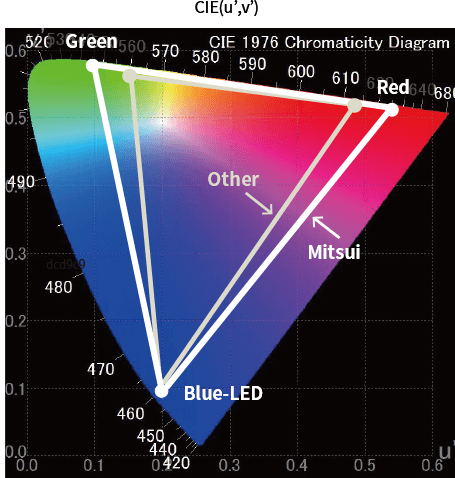
Our new own-developed process results in highly luminescent, highly durable phosphors regardless of the particle size — materials which are helping turn displays with superior color reproducibility into reality.
Application
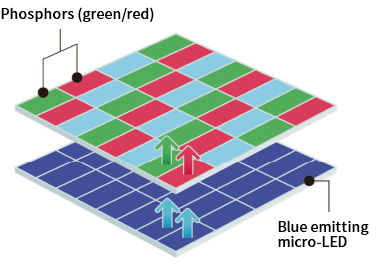
Color conversion material for micro LED displays
Micro-LED
Micro-LED displays, manufactured with a micro-LED for each pixel element, are attracting attention as the next generation of displays.
In contrast to conventional liquid crystal displays, in which a white light from the backlight is filtered out by color filters to produce each RGB color, micro-LED displays efficiently utilize light to readily produce outstanding brightness. Additional features of micro-LEDs are high contrast due to self-luminescence, together with a wide viewing angle.
To facilitate the widespread adoption of micro-LED displays, it is imperative to increase the number of chips produced from a single wafer. Consequently, each LED chip must be miniaturized.
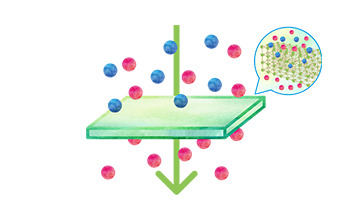
Whereas miniaturization causes the efficiency of green and red LED chips to drop, blue LEDs maintain their high efficiency even when miniaturized. The use of color converting materials to convert the light emitted from blue LEDs provides a way to still achieve a full color range with miniaturized chips.
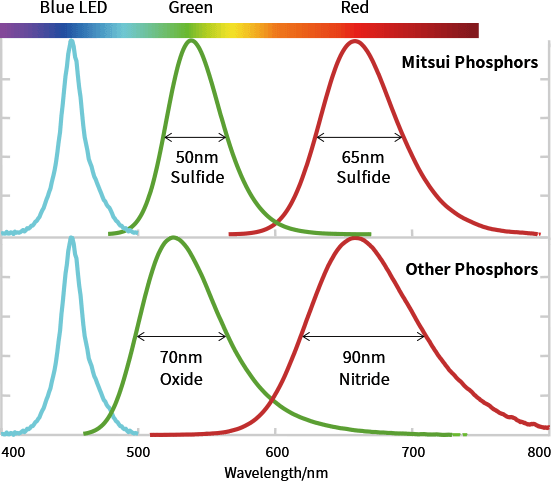
Our fine-particle, highly luminescent sulfide phosphors are among the best candidates for color converting materials for this type of micro-LED display.
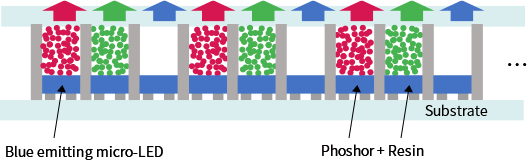

To promote the spread of micro-LED displays,
Mitsui Kinzoku is an active member of the Micro-LED Association.
Color converting films for liquid crystal backlights
Phosphor films
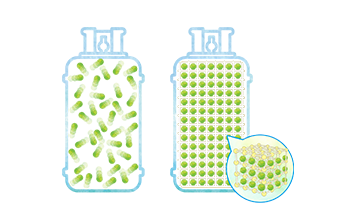
Color converting films using QD (quantum dots) are utilized in liquid crystal backlights to create displays with high color reproducibility.
Although QD provide a narrow luminescent half-width and high color purity luminescence, the ease with which they react with moisture in the air makes them unreliable, necessitating the use of expensive barrier films.
Our sulfide phosphors use Mitsui Kinzoku own-developed coating technology, removing the need for a barrier film.
Furthermore, while some QD contain cadmium and other substances regulated by RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive), our phosphors are free of such type of harmful substances.


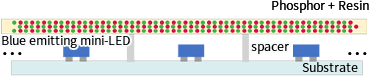
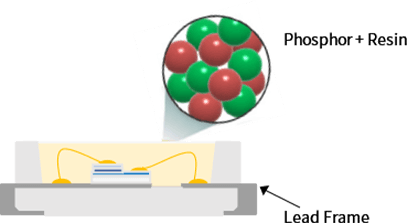
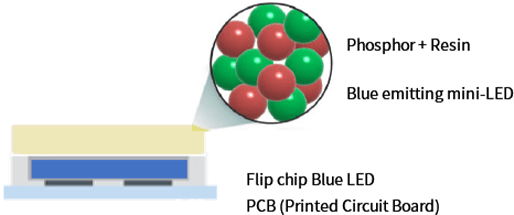
Color converting materials for white LED
LED packaging (phosphor on chip)
Silver has traditionally been used in LED packaging as a reflector and lead frame material. Silver reacts readily with sulfide phosphors to form silver sulfide, reducing the reflectivity inside the package which results in a drop in LED efficiency. As LED packaging has evolved, silver-free versions have recently appeared — for which concerns about a drop in reflectivity caused by silver corrosion no longer exist. In combination with our narrow half-width sulfide phosphors, these recent versions are anticipated to deliver white LED packaging with high brightness and a wide color field.

Document download (characteristic data, etc.)
Corporate Venture Capital
We pursue co-creation of new businesses
through collaboration with startups.

Business Fields of Focus
New Materials
Download a Document
Click category to download