Mitsui Kinzoku is engaging in the development of high-quality Cu sinter paste by capitalizing on its metal powder management technologies developed during many years of handling copper powder. Product promotion is targeted in fields such as electric vehicles (EV) where power device performance is key.
What is the current position regarding the creation of a commercial product?
We are now one step before commercialization, getting customers to test our submitted samples which, upon their acceptance, we will formally convert into products.
Please tell us the story of the development
The process has not been straightforward but the development of a bonding material for power devices started around 2016. The AST Business Promotion Unit, our current set-up, started operating in 2020.
As mentioned earlier, the next generation power semiconductors, typified by silicon carbide, can operate at high temperatures, but solder has its limitations. In contrast, sinter pastes do not melt even in severe heating environments, have good thermal conductivity, are highly suitable as bonding materials for next generation semiconductors, and have the advantage of being lead-free.
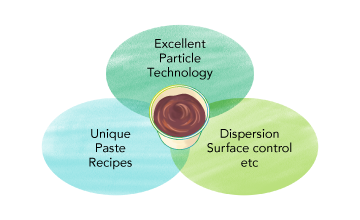
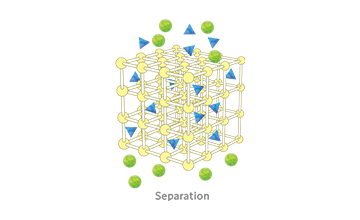
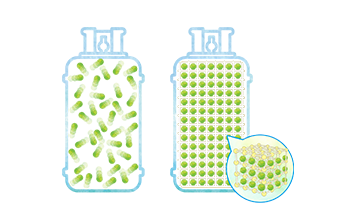
We decided to focus on Cu sinter paste because Mitsui Kinzoku has a long history of handling metal powders. The properties of a sinter paste can be controlled by the properties of its constituent powder. Copper particles therefore hold the key to Cu sinter paste. One of the reasons we started working on Cu sinter paste was that we were confident we could create good material by capitalizing on the technologies and techniques Mitsui Kinzoku has accumulated as a handler of copper powder.
In which areas are general consumers most likely to notice changes once the use of Cu sinter paste has become established?
Among everyday things, one such area is likely to be electric vehicles (EV). The more widespread the usage of electricity in a vehicle, and that includes hybrids, the greater the importance of power devices becomes. As the use of gasoline disappears, talk of fuel consumption will switch to “electricity consumption”, which should get better. Electrical energy efficiency is strongly influenced by power device performance. So, if we can use heat resistant and highly reliable components, device performance will increase over time, leading to expectations of better EV performance and cost benefits. This is why I think that the influence will be felt first in the EV field.
Improved conversion efficiency is a hot topic also in the electricity generation and supply fields. So perhaps consumers will also notice changes in, for example, the spread and utilization of renewable energy. Besides that, power semiconductors will certainly start to be utilized to meet conversion related demands for miniaturization.
In this way, by also getting involved in fields of electricity usage not connected to EV, I think our technology has a role to play in enabling people to use electricity safely and securely.
With Mitsui Kinzoku proceeding to convert Cu sinter paste into a commercial product, when do you expect it to be launched?
Due to stronger regulation in future of automotive exhaust gases, especially in the EU and the United States, the expansion of EV is expected to proceed as sales of ICE (internal combustion engine) vehicles decline in the run up to 2035. Considering this, I think 2025 or thereabouts could mark a critical point in time. While we do not expect Mitsui Kinzoku products to immediately spread into the market at that time, we believe Cu sinter paste can gradually start to contribute. Therefore, while we firstly aim to get customers to accept our material, we view 2027 or 2028 as a suitable timing for wider expansion into the market.
[continued in Part 3]
Interviewee: Shinichi Yamauchi, Technology and Development Group Leader, AST Business Promotion Unit, Business Creation Sector, Mitsui Mining & Smelting Co., Ltd.
(Date of interview: February 21, 2023)
(The company is hereinafter referred to as "Mitsui Kinzoku.")